Introduction
The Indian Republic’s annual budget is known as the Union Budget. Every year, it is usually represented in February by the Union Finance Minister. The final full-fledged budget of the present government before the upcoming Lok Sabha elections, which are scheduled for 2024, was delivered by Union Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman on February 1st, 2023.
Sitharaman highlighted significant modifications to the tax slabs under the new tax regime as well as a significant increase in funding for railways and capital expenditures, which will greatly benefit taxpayers and the economy.

Constitutional Provisions
The Indian Constitution’s Article 112 refers to the Union Budget of a year as the Annual Financial Statement (AFS). It is a statement of the government’s expected receipts and expenditures for a certain fiscal year (which begins on 1st April of the current year and ends on 31st March of the following year).
The nodal institution in charge of creating the budget is the Department of Economic Affairs under the Ministry of Finance.
Highlights of Budget 2023-24
The previous tax system has not changed.
New tax regime to become the default tax regime. The old tax system is still an option for citizens, though.
No tax on income up to Rs 7.5 lakh a year in the new tax regime (with inclusion of standard deduction)
In the new tax system, the government wants to lower the maximum surcharge rate from 37% to 25%.
New Income Tax Slabs Under New Tax Regimes:
- Rs 0-3 lakh: Nil
- Rs 3-6 lakhs: 5%
- Rs 6-9 lakhs: 10%
- Rs 9-12 lakhs: 15%
- Rs 12-15 lakhs: 20%
- Rs Over 15 lakhs: 30%
- Taxes for an individual income of Rs 9 lakh a year will only be Rs 45,000: Sitharaman, FM
- Tax on income of Rs 15 lakh is reduced to Rs 1.5 lakh from Rs 1.87 lakh.
- A basic deduction of Rs 50,000 has been made available to taxpayers under the new system.
- Payment from the Agniveer Corpus Fund received by Agniveers will be exempt.
- Insurance policies with premiums over Rs. 5 lakh are no longer free from taxes.
- The government wants to make sure that net wins from online games are taxed at the moment of withdrawal or at the end of the fiscal year by instituting TDS.
- Tax-free leave encashment for non-government salaried workers has increased from Rs 3 lakh to Rs 25 lakh.
- The TDS on cash withdrawal would have a higher cap of Rs 3 crore for cooperative organisations.
- A new version of the Common IT Return Form will be released for the benefit of taxpayers.
- Grievance redressal mechanism to be strengthened.
- TDS rate to be reduced from 30 percent to 20 percent on the taxable portion of EPF withdrawal in non-PAN cases.
Cheaper
- Mobile phones
- TV
- Lab-grown diamonds
- Shrimp feed
- Machinery for lithium-ion batteries
- Raw materials for the EV industry
Costlier
- Cigarettes
- Silver
- Compounded rubber
- Imitation Jewellery
- Articles made from gold bars
- Imported bicycles and toys
- Imported kitchen electric chimney
- Imported luxury cars and EVs
Indirect Taxes
- A tax increase of 16% on certain cigarettes
- Up to March 2024, new cooperatives that start production would pay 15% less in taxes.
- Glycerine and crude oil now only carry a 2.5% general customs duty.
- Silver bar import taxes increased to match those of gold and platinum
- Customs tax reductions on imports of mobile phone parts should be extended by a year.
- Customs duty on open TV panel cells has been cut to 2.5% in order to encourage TV production.
- Customs duty on the import of certain components and inputs, such as camera lenses, is waived
- Extension of the one-year concessional duty on lithium-ion batteries
- Number of basic custom duty rates on goods other than textiles and agriculture reduced from 21 to 13. As a result, there are minimal tax modifications for several goods, including toys, bicycles, and cars.
Saving schemes announcements
- The Senior Citizen Savings Scheme’s maximum deposit amount would increase from Rs. 15 lakh to Rs. 30 lakh.
- Limits for joint accounts under the Monthly Income Scheme have been raised to Rs. 9 lakh and Rs. 15 lakh.
- Mahila Samman Saving Certificate, a one-time new saving programme for women, will be made available for 2 years, through March 2025.
- The scheme would offer a deposit facility of up to Rs 2 lakh for a 2-year term with a fixed interest rate of 7.5% and the option of a partial withdrawal in the name of women or girls.
Railways get a massive boost:
- In FY24, a budget of Rs 2.4 lakh crore was allocated for the railways.
- It is about nine times higher than the allocations for FY14 and is the highest allocation for Railways ever.
- This year, a total of Rs 17,296.84 crore has been allotted for track renewal, higher than Rs 15,388.05 crore in RE 2022-23.
- By August 2023, the Railways would probably have introduced 75 Vande Bharat trains.
Capex hiked by 33%
- To increase the economic potential and job creation, attract private investment, and act as a buffer against global headwinds, the government has announced a capital investment of Rs 10 lakh crore, a steep increase of 33% for the third year in a row.
- The Centre will effectively spend Rs 13.7 lakh crore on capital.
- 3% of GDP is projected for capital investment in FY24.
- In FY24, the Center’s actual capital investments were Rs 13.7 lakh.
- In order to increase options for private investment in infrastructure, a new Infrastructure Finance Secretariat has been established.
Defence Budget hiked by 13%:
- From Rs., 5.25 lakh crore last year, the defence budget jumped to Rs. 5.94 lakh crore this year.
- The Rs. 1.62 lakh crore budgeted for capital expenses covers the acquisition of new weapons, aircraft, warships, and other military hardware.
- The budgetary allotment for capital outlay for 2022–2023 was Rs. 1.52 lakh crore.
- The Border Roads Organization’s capital budget increased to Rs 5,000 crore.
- The Indian Air Force incurred the largest capital expenditure, totaling Rs 57,137.09 crore.
- The Indian Navy received a capital outlay budget of Rs 52,804 crore.
- The Army’s capital expenditure is estimated to reach Rs 37,241 crore.
- The amount allotted to the Defence Research and Development Organization (DRDO) is estimated at Rs 23,264 crore.
Fiscal position:
- By 2025–2026, the fiscal deficit is expected to be less than 4.5%.
- In the Revised Estimate for FY23, the objective for the fiscal deficit was kept at 6.4%; for FY24, it was cut to 5.9%.
- In FY24, gross market borrowing was estimated at Rs 15.43 lakh crore.
- At Rs 11.8 lakh crore, net market borrowing was recorded for FY24.
- The revised estimate for FY23 net tax collections is Rs 20.9 lakh crore.
- The updated estimate for FY23 overall expenditure is Rs. 41.9 lakh crore.
- Total receipts other than borrowing estimated at Rs 24.3 lakh crore for FY23.
- Net tax collections for FY24 were $23.3 lakh crore.
MSME
- A revised credit guarantee for MSMEs would go into effect on April 1, 2023, with a corpus infusion of Rs 9,000 crore.
- The plan would permit an additional Rs 2 lakh crore of collateral-free guaranteed lending while also lowering the cost of the credit by roughly 1%.
Jobs:
- Pradhan Mantri Kaushal 4.0 Vikas Yojana will be launched by the government.
- 30 Skill India International Centers will be built throughout various States to prepare young people for opportunities abroad.
- Under a pan, Direct Benefit Transfer 47 lakh young people would receive stipend support through the India National Apprenticeship Promotion Scheme over the course of three years.
Gems and Jewellery:
An IIT will get a five-year research and development funding in order to promote domestic manufacturing of lab-grown diamonds. In Part-B of the budget paper, a proposal to revise the customs duty on lab-grown diamonds is included.
Digital services
- Expanding the scope of services offered by DigiLocker.
- Engineering colleges will establish up 100 labs for researching 5G applications.
- Precision farming, smart classrooms, and healthcare applications will all be covered in labs.
- Projects to launch Phase 3 of E-courts with an investment of Rs 7,000 crore.
- Leading business actors will collaborate to create scalable solutions for the health, agricultural, and other sectors.
Education:
- Three artificial intelligence centres of excellence will be established in leading universities.
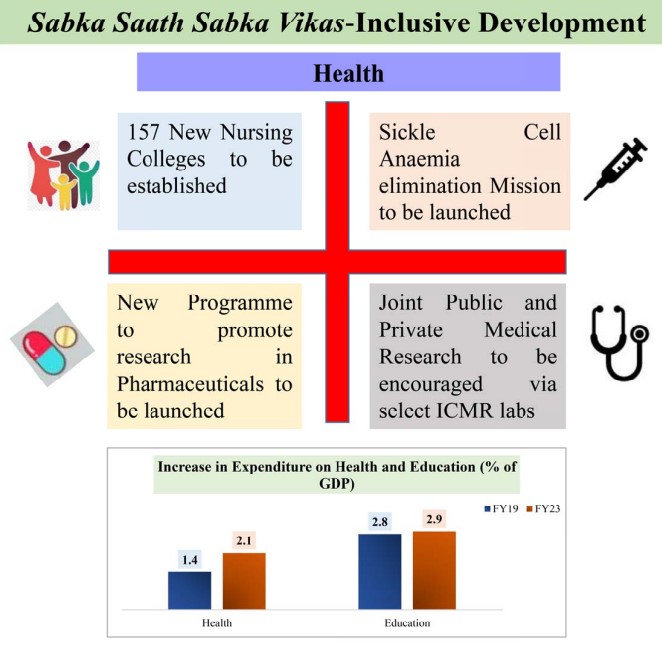
- Alongside the 157 medical colleges that have already been operating since 2014, 157 new nursing colleges will also be founded.
- In the upcoming three years, Eklavaya Model Residential Schools will be established. 38,800 teachers and support staff will be hired by the Center to work in 740 schools that will serve 3.5 lakh tribal students.
- A national data governance policy will be released to encourage scholarly and entrepreneurial research and innovation.
- A grant increase of Rs 459 crores has been made to the University Grants Commission (UGC) (9.37 pc).
- In comparison to BE 2022–23, support for Central Universities has increased by 17.66%, for Deemed Universities by 27%, IITs by 14%, and NITs by 10.5%.
Seven priorities of the Budget, ‘Saptarishi’:
Health:
- The Union Budget includes Rs 89,155 crore for the health sector.
- the goal of eradicating sickle cell disease by 2047.
- The industry will be encouraged to make research investments as a result of the formulation of a new pharmaceutical research program.
- The Department of Health and Family Welfare will receive 86,175 crores of the total budget of Rs. 89,155 crores, while the Department of Health Research will receive 2,980 crores.
- The Pradhan Mantri Swasthya Suraksha Yojana will have a budget of Rs 3,365 the crore years 2023–2024.
- The National Health Mission’s budget allocation has grown from Rs 28,974.29 crore, one of these central sector initiatives.
- The AYUSH ministry’s budget allotment has increased from Rs 2,845.75 crore.
- The National Digital Health Mission’s budget has increased from Rs 140 crore to Rs 341.02 crore.
Conclusion
The Finance Minister asserted that a number of achievements, including the world-class digital public infrastructure projects Aadhaar, Co-Win, and UPI; the unprecedented scale and speed of the COVID-19 vaccination drive; and India’s proactive role in frontier areas such as achieving the goals of mission LiFE and the National Hydrogen Mission, have contributed to the country’s rising international profile.
She said that through a programme to provide free food grains to more than 80 million people for 28 months during the Covid-19 pandemic, the government made sure that nobody went to bed hungry. The Minister continued by saying that, as part of the Center’s ongoing commitment to ensuring food and nutritional security, the government will begin implementing a programme on January 1, 2023, to provide free food grain to all Antyodaya and priority homes for the following year.
Get in touch for any kind of help and information
Legal Door one of the best team of Lawyer in Noida who provide top class legal services also top rated advocate in Gaur City, Noida.
Our head office address:
O-402, 4th Floor, Addela Mart, Raksha Addela, Gaur City 2, Greater Noida West, G.B. Nagar, U.P. – 201318
Call for help:
+91-9811765737
Mail us for information
info@legaldoor.in
legaldoorindia@gmail.com







